In anatomy, the transverse ligament of the atlas is a ligament which arches across the ring of the atlas (the topmost cervical vertebra, which directly supports the skull), and keeps the odontoid process in contact with the atlas.
Anatomy
It is concave in front, convex behind, broader and thicker in the middle than at the ends, and firmly attached on either side to a small tubercle on the medial surface of the lateral mass of the atlas.As it crosses the odontoid process, a small fasciculus (crus superius) is prolonged upward, and another (crus inferius) downward, from the superficial or posterior fibers of the ligament.The former is attached to the basilar part of the occipital bone, in close relation with the membrana tectoria; the latter is fixed to the posterior surface of the body of the axis; hence, the whole ligament is named the cruciate ligament of the atlas.The transverse ligament divides the ring of the atlas into two unequal parts: of these, the posterior and larger serves for the transmission of the medulla spinalis and its membranes and the accessory nerves; the anterior and smaller contains the odontoid process.The neck of the odontoid process is constricted where it is embraced posteriorly by the transverse ligament, so that this ligament suffices to retain the odontoid process in position after all the other ligaments have been divided. [Source: Wikipedia 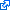 ]
]